In the age of rapid urbanization and rising vehicle ownership, parking has emerged as one of the most persistent and frustrating challenges in modern cities. Anyone who has circled city blocks in search of an open parking space knows the stress, time-waste, and environmental impact of inefficient parking infrastructure. Fortunately, the convergence of artificial intelligence (AI) and sensor technologies is revolutionizing the way we manage and utilize parking resources. At the core of this transformation lies the smart parking system—an intelligent, data-driven approach powered by smart parking software and sensor integration.
The Urban Parking Crisis
To understand the importance of smart parking, we first need to grasp the scale of the parking problem. In cities like New York, London, or Mumbai, the demand for parking often exceeds supply, especially during peak hours. Studies estimate that drivers spend an average of 17 hours a year searching for parking, wasting fuel and contributing to traffic congestion and air pollution.
Traditional parking infrastructure is static and inefficient, offering little visibility into real-time space availability or usage patterns. Without data, cities and businesses cannot optimize parking allocations or pricing, and drivers remain in the dark.
Enter smart parking systems, which provide real-time, intelligent, and automated parking management solutions.
What Is a Smart Parking System?
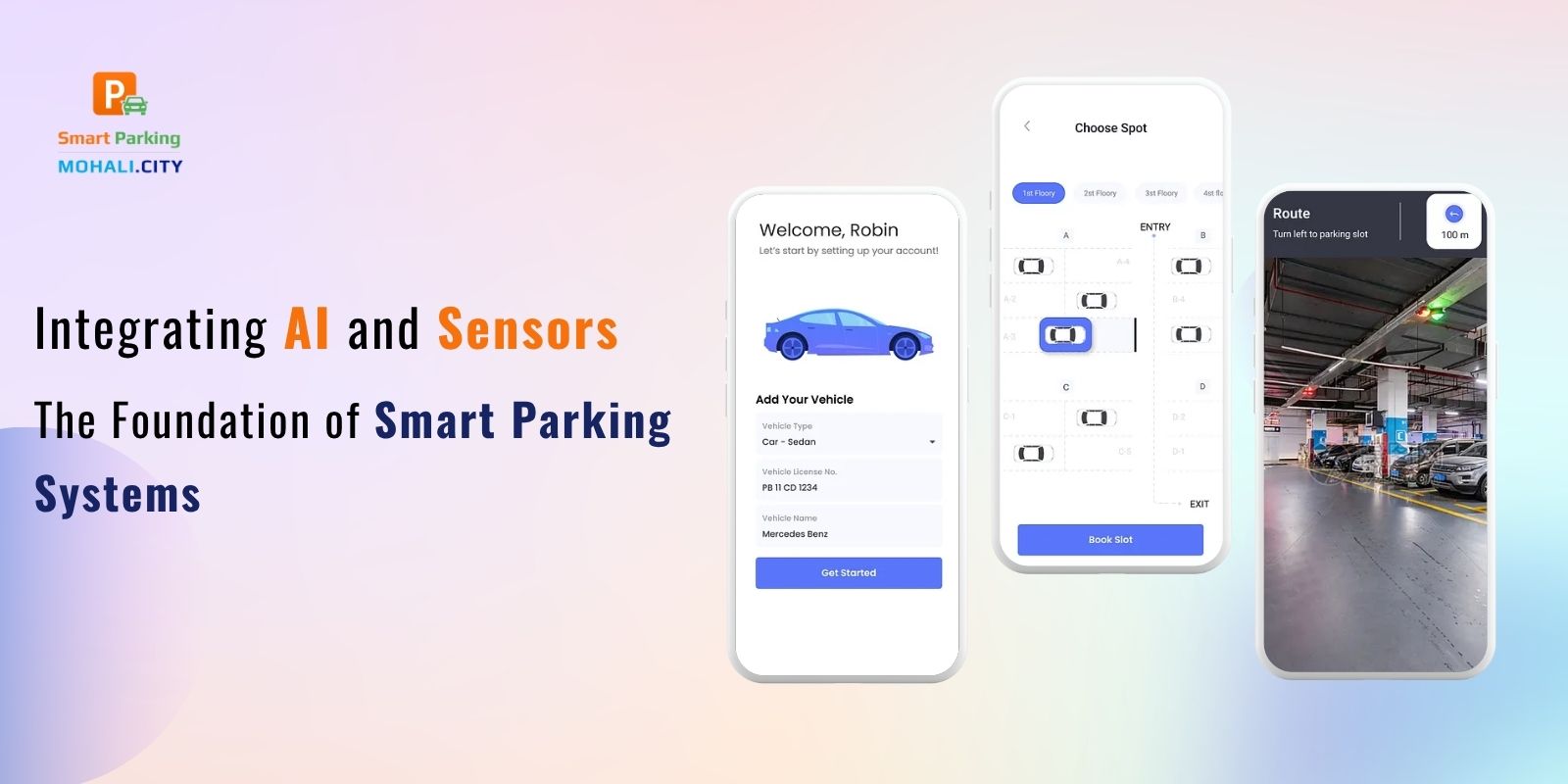
A smart parking system uses a combination of sensor hardware, software platforms, and AI algorithms to monitor and manage parking spaces. These systems enable real-time updates on parking availability, automate enforcement, guide drivers to open spots, and provide analytics to operators for optimizing infrastructure and revenue.
The core components include:
- Sensors to detect vehicle presence.
- IoT connectivity to transmit data.
- Smart parking software to process data and provide insights.
- User interfaces, typically mobile apps or digital displays.
- AI algorithms for pattern recognition, demand forecasting, and automation.
By transforming static parking lots into dynamic systems, smart parking solutions are helping cities address traffic congestion, reduce emissions, improve user experience, and optimize resource utilization.
The Role of Sensors in Smart Parking Systems
Sensors are the frontline technology of any smart parking setup. These devices are deployed in or around parking spaces to detect the presence or absence of vehicles. There are several types of sensors used in smart parking:
1. Ultrasonic Sensors
These are installed above or in-ground and work by emitting sound waves that bounce back when they hit an object. The time it takes for the sound to return helps determine whether a parking spot is occupied.
2. Infrared Sensors
These detect heat signatures and movement. They are effective in both indoor and outdoor settings and are often used in combination with cameras.
3. Magnetic Sensors
Installed in the ground, these detect changes in the Earth's magnetic field caused by metal objects like cars. They are durable and ideal for outdoor use.
4. Camera-Based Sensors
Cameras offer visual monitoring and can integrate with AI to perform license plate recognition, vehicle tracking, and occupancy detection. They can cover multiple parking spaces with a single unit.
All these sensors feed data to the central smart parking software, which processes it and relays real-time information to users and administrators.
AI: The Intelligence Behind Smart Parking Software
While sensors gather raw data, it’s AI that transforms that data into actionable insights. Integrated into smart parking software, AI plays multiple critical roles:
1. Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
AI processes data from sensors to monitor parking occupancy in real-time. It updates availability across user interfaces—apps, digital signs, and web dashboards—so drivers can locate spots quickly.
2. Predictive Analytics
AI doesn’t just analyze current conditions; it learns from historical patterns. It can predict high-demand periods, suggest optimal parking durations, and anticipate space turnover rates. These insights allow better planning for both operators and users.
3. Dynamic Pricing
Using demand prediction and real-time data, AI enables dynamic pricing models. Parking rates can fluctuate based on time of day, occupancy levels, and event schedules. This not only maximizes revenue for operators but also balances usage across lots.
4. Automation and Control
AI facilitates automation in ticketing, payments, and access control. It can authorize or deny access, calculate parking fees, and trigger security alerts, minimizing the need for human intervention.
5. License Plate Recognition (LPR)
AI-powered image recognition systems allow seamless vehicle entry and exit through license plate scanning. This supports contactless payments and enhances security.
How AI and Sensors Work Together
The real magic of a smart parking system lies in the interplay between AI and sensors. Here's how a typical system works:
- Sensor Detection: Sensors detect whether a space is occupied.
- Data Transmission: Sensor data is transmitted to a centralized system via IoT protocols.
- AI Processing: AI in the smart parking software analyzes this data to determine space availability, monitor trends, and predict future patterns.
- User Guidance: The processed data is then shared with users via apps, guiding them to the nearest available spots.
- Management Interface: Parking administrators get access to dashboards with real-time monitoring, usage trends, and financial reporting.
Together, AI and sensors create a closed-loop system that is intelligent, responsive, and scalable.
Key Benefits of Smart Parking Systems
The implementation of smart parking systems delivers tangible benefits to both users and parking operators:
For Drivers:
- Reduced search time: Real-time updates eliminate the need to circle blocks looking for parking.
- Increased convenience: Automated payments, reservations, and navigation make parking seamless.
- Lower emissions: Less driving means reduced carbon footprint and fuel consumption.
For Operators:
- Better space utilization: Accurate data allows for improved planning and allocation.
- Higher revenue:Dynamic pricing and higher occupancy rates increase profitability.
- Operational efficiency: Automated enforcement and monitoring reduce labor costs.
For Cities:
- Less traffic congestion: Smart parking helps reduce unnecessary driving.
- Improved air quality: Lower vehicle emissions contribute to cleaner air.
- Data-driven urban planning: Parking data helps city planners design better transport infrastructure.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the benefits, integrating AI and sensors into parking infrastructure comes with challenges:
- High Initial Costs: Installing sensors and developing smart software requires capital investment.
- Technology Integration:Legacy infrastructure may not be compatible with modern systems.
- Data Privacy: LPR and surveillance data must be secured and comply with privacy regulations.
- Maintenance: Sensors and IoT devices require regular upkeep to ensure reliability.
Overcoming these hurdles involves careful planning, vendor selection, and ongoing support.
The Future of Smart Parking
As AI continues to evolve and sensor technology becomes more advanced and affordable, the future of smart parking systems looks promising. Some emerging trends include:
- Autonomous Vehicle Integration: Smart parking systems will soon need to interact with self-driving cars, providing automatic space allocation and charging services.
- EV Charging Integration: Smart parking spots equipped with EV chargers and AI-driven usage forecasting will become more common.
- Blockchain and Payments: Secure, transparent transactions for parking using blockchain could eliminate disputes and fraud.
- Augmented Reality Navigation: Future apps may guide drivers using AR overlays for enhanced visual navigation.
Conclusion
The integration of AI and sensors has laid the foundation for the modern smart parking system. These systems are not just solving a logistical problem—they are reshaping urban mobility and paving the way for smarter, greener, and more connected cities. With the continued evolution of smart parking software, cities and private operators alike can look forward to more efficient operations, satisfied users, and a reduced environmental footprint.
Adopting smart parking is no longer a futuristic dream—it’s a necessary step toward sustainable urban living. As cities strive to become smarter and more livable, integrating AI and sensor technologies into parking management will play a pivotal role in that transformation.










Share this post on: